02:01
With complex design ideation, it can be useful to use various math functions to control geometry. To this end, Onshape has numeric fields built in directly to dialog boxes. The following table summarizes these functions and operators:
Functions | ||
Name | Syntax | Examples |
Absolute Value | abs(x) | abs(-3) = 3 |
Ceiling | ceil(x) | ceil(4.75) = 5 |
Clamp | clamp(x, min, max) | clamp(x,1,10) will allow for x to vary between 1 and 10 freely but never go above or below. |
Exponential Function | exp(x) | exp(2) = 7.389 |
Floor | floor(x) | floor(4.75) = 4 |
Hypotenuse | hypot(x,y) | hypot(3,4) = 5 |
Logarithm - Natural (ln) | log(x) | log(10) = 2.303 |
Logarithm - Common | log10(x) | log10(10) = 1 |
Minimum | min(x,y) | min(2,5) = 2 |
Maximum | max(x,y) | max(2,5) = 5 |
Round | round(x) | round(3.50002) = 4 |
Square Root | sqrt(x) | sqrt(4) = 2 sqrt(100) = 10 |
Functions
Name
Syntax
Examples
Absolute Value
abs(x)
abs(-3) = 3
Ceiling
ceil(x)
ceil(4.75) = 5
Clamp
clamp(x, min, max)
clamp(x,1,10) will allow for x to vary between 1 and 10 freely but never go above or below.
Exponential Function
exp(x)
exp(2) = 7.389
Floor
floor(x)
floor(4.75) = 4
Hypotenuse
hypot(x,y)
hypot(3,4) = 5
Logarithm - Natural (ln)
log(x)
log(10) = 2.303
Logarithm - Common
log10(x)
log10(10) = 1
Minimum
min(x,y)
min(2,5) = 2
Maximum
max(x,y)
max(2,5) = 5
Round
round(x)
round(3.50002) = 4
Square Root
sqrt(x)
sqrt(4) = 2
sqrt(100) = 10
Trigonometric Functions | ||
Name | Syntax | Examples |
Sine | sin(x) | sin(30) = 0.5 |
Hyperbolic Sine | sinh(x) | sinh(1) = 1.175 |
Arcsine | asin(x) | asin(1) = 90 deg (must be used in appropriate field) |
Hyperbolic Arcsine | asinh(x) | asinh(1) = 0.881 |
Cosine | cos(x) | cos(30) = 0.866 |
Hyperbolic Cosine | cosh(x) | cosh(1) = 1.543 |
Arccosine | acos(x) | acos(1) = 0 |
Hyperbolic Arccosine | acosh(x) | acosh(2) = 1.317 |
Tangent | tan(x) | tan(30) = 0.577 |
Hyperbolic Tangent | tanh(x) | tanh(1) = 0.762 |
Arctangent & Arctangent2 | atan(x) atan2(x,y) | atan(1) = 45 deg atan2(1,2) = 26.565 deg |
Trigonometric Functions
Name
Syntax
Examples
Sine
sin(x)
sin(30) = 0.5
Hyperbolic Sine
sinh(x)
sinh(1) = 1.175
Arcsine
asin(x)
asin(1) = 90 deg (must be used in appropriate field)
Hyperbolic Arcsine
asinh(x)
asinh(1) = 0.881
Cosine
cos(x)
cos(30) = 0.866
Hyperbolic Cosine
cosh(x)
cosh(1) = 1.543
Arccosine
acos(x)
acos(1) = 0
Hyperbolic Arccosine
acosh(x)
acosh(2) = 1.317
Tangent
tan(x)
tan(30) = 0.577
Hyperbolic Tangent
tanh(x)
tanh(1) = 0.762
Arctangent & Arctangent2
atan(x)
atan2(x,y)
atan(1) = 45 deg
atan2(1,2) = 26.565 deg
Misc/Operations | ||
Modulo Operator | x%y | 6%2 = 0 6%4 = 2 6%5 = 1 |
Array | [0,1,2,3,4][n] | [1,4,7,8,23,7][0] = 1 [1,4,7,8,23,7][3] = 8 |
Misc/Operations
Modulo Operator
x%y
6%2 = 0
6%4 = 2
6%5 = 1
Array
[0,1,2,3,4][n]
[1,4,7,8,23,7][0] = 1
[1,4,7,8,23,7][3] = 8
Numeric fields are powerful by themselves. However, their true power comes from how creatively a Part Studio or Onshape Document can be architected to automate some of the math that is inevitably a part of design. A quick example would be to combine variables and configurations with numeric fields.
For this example, I’ll use the Clamp function to show how to use equations to generate a bounding box for a variable. To start, I’ve created a sheet metal plate with a single hole:
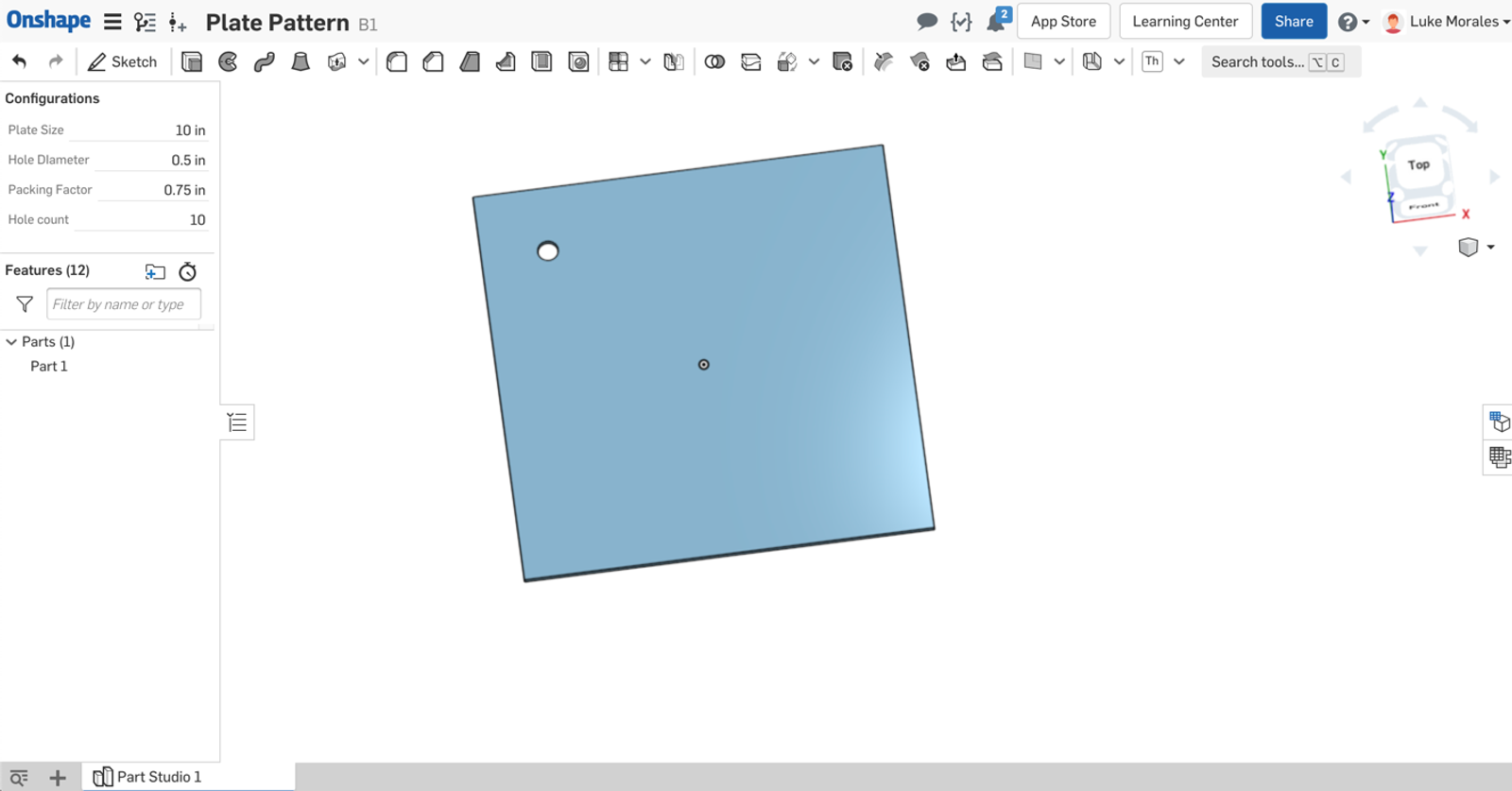
I have a combination of configuration variables and parametric variables in this Part Studio. The configuration variables will control the plate size (#Size), hole diameter (#Hole_Diameter), distance between holes (#Packing_Factor), and number of holes per row (#Hole_count).
I want to create a pattern of this hole that changes based on these configurations. However, linear patterns are not “smart” in so far as the scope of patterning “up to” a certain point. Thus, the following method is used.
First, I create two parametric variables: #HoleClamp and #Edge. #Edge is just the calculation of the space on either end of the row using #Hole_count and #Packing_Factor. The real magic happens with the #HoleClamp variable; its definition is as follows:
clamp(#Hole_count,2,floor(((#Hole_Diameter-#Size)/(-#Packing_Factor))))
This is then set as the instance count for a linear pattern of the hole. As the #Hole_Count configuration variable is changed, the clamp ensures that the pattern never exceeds the carrying capacity of the plate given the other dimensions specified by configurations.
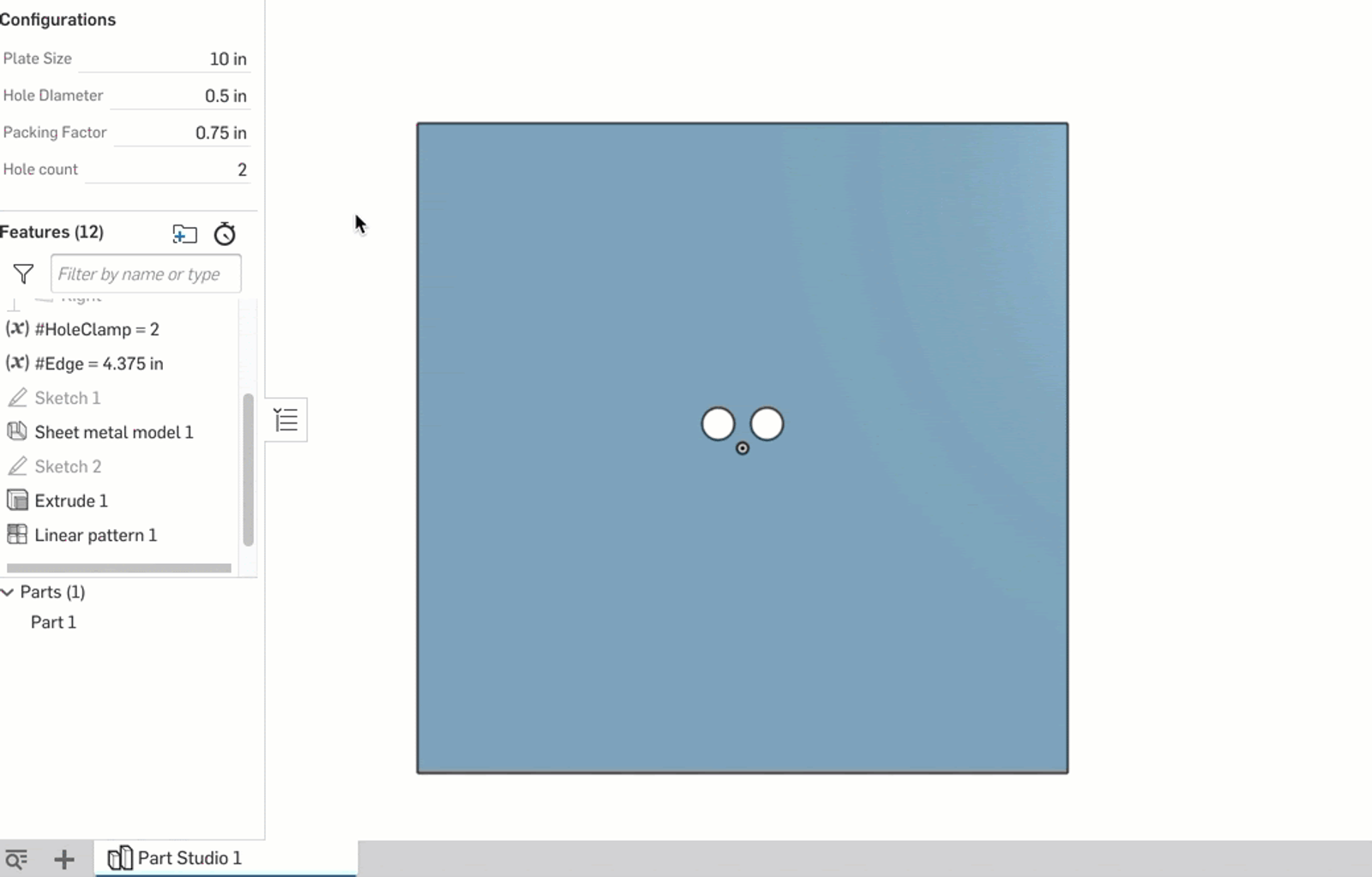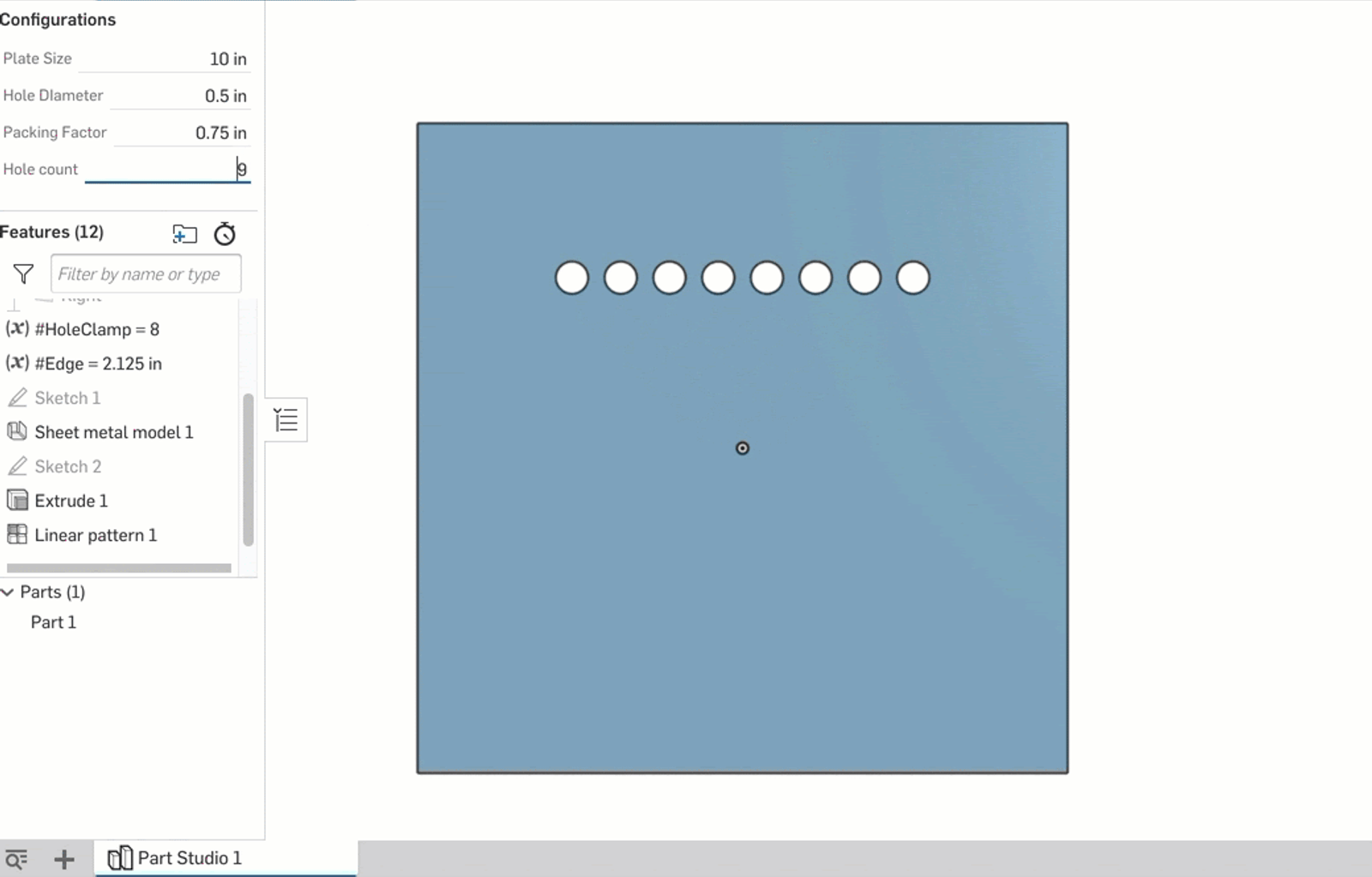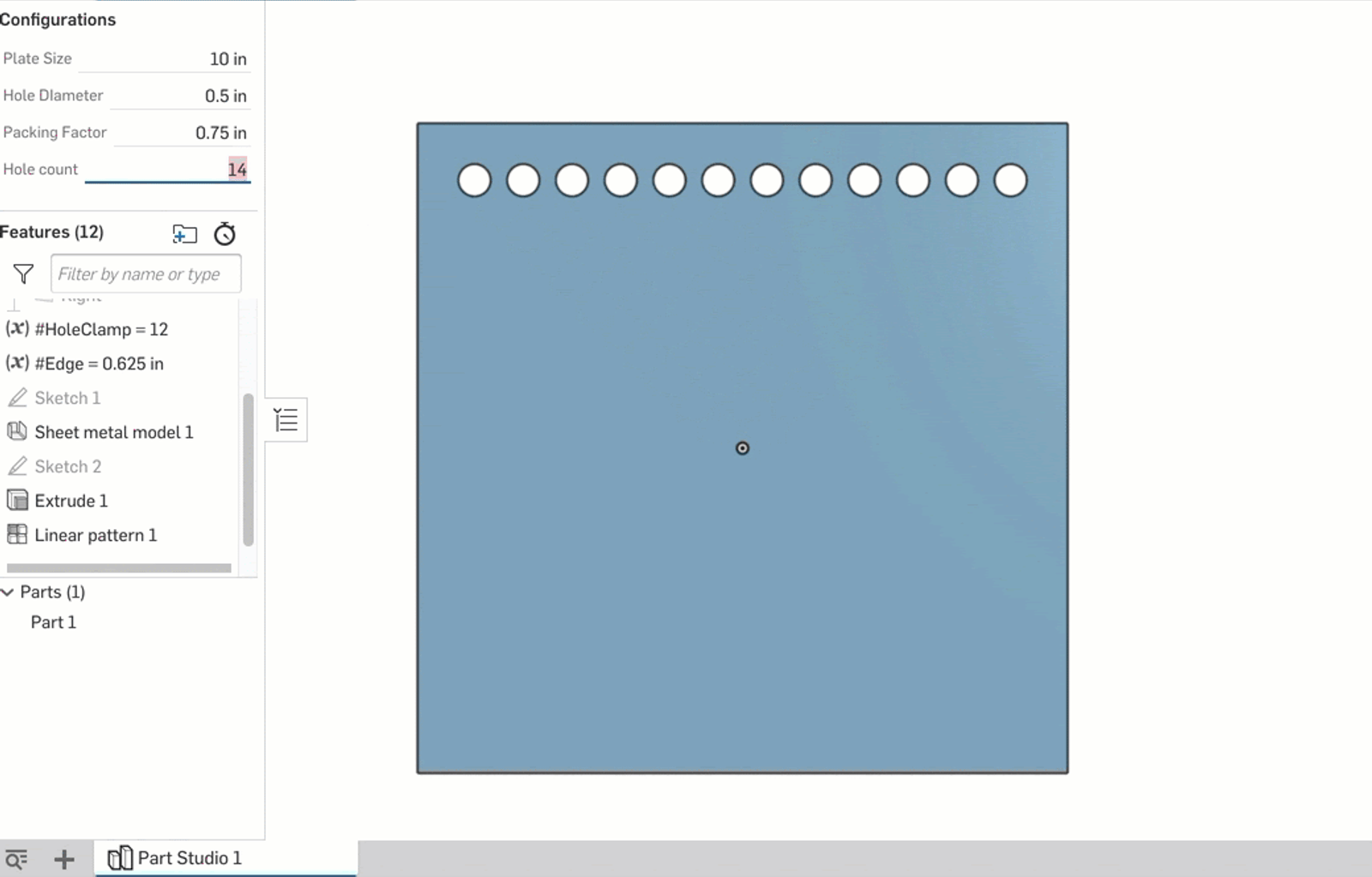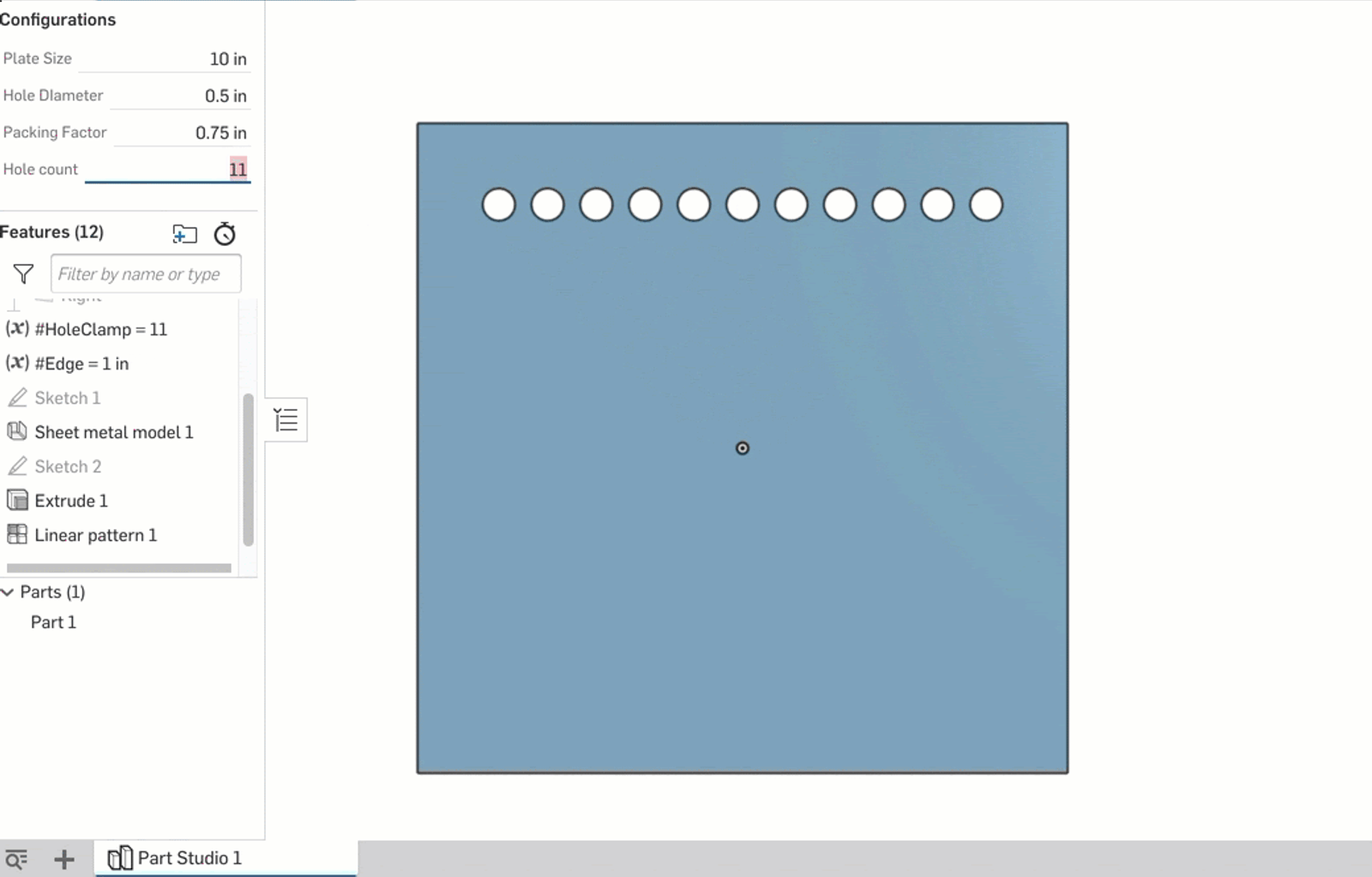
This is a good way to leverage the accessibility of the configuration variable while adding a minimum and maximum that are governed by variable equations.
Following the same logic, two more parametric variables are created: #HoleClamp2 and #Edge2 which are driven by a new configuration variable, #Row_Count. The final product behaves like this:
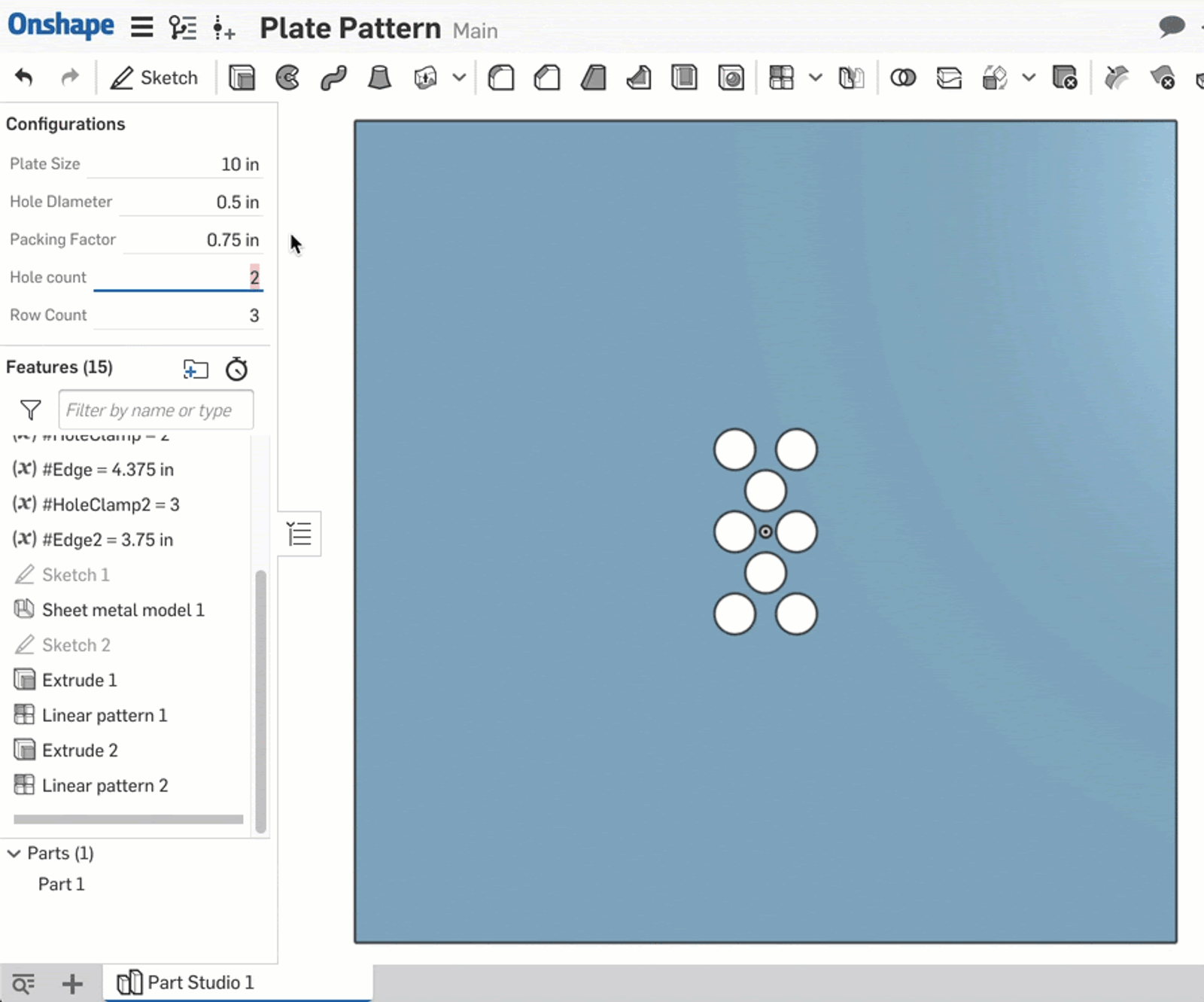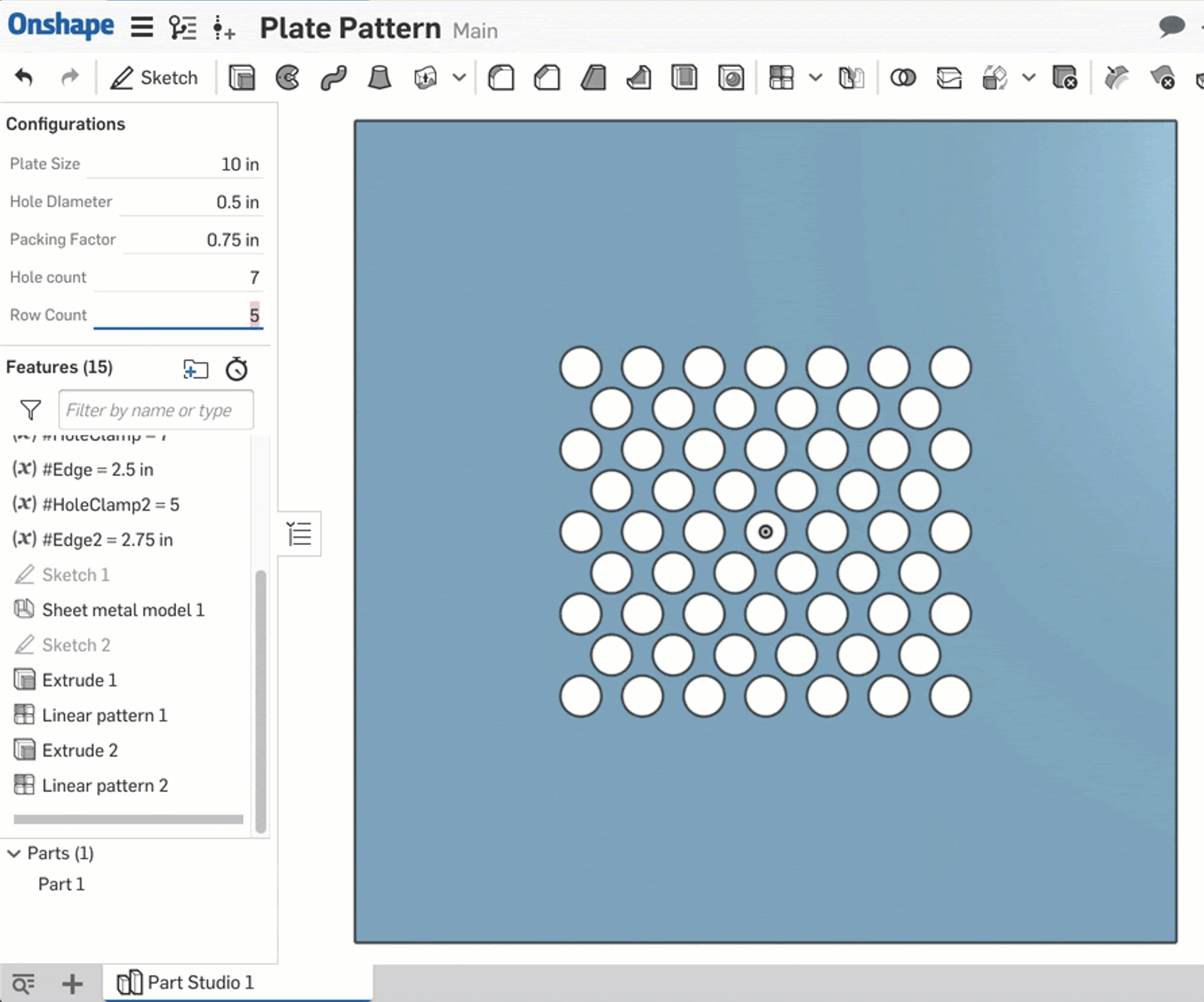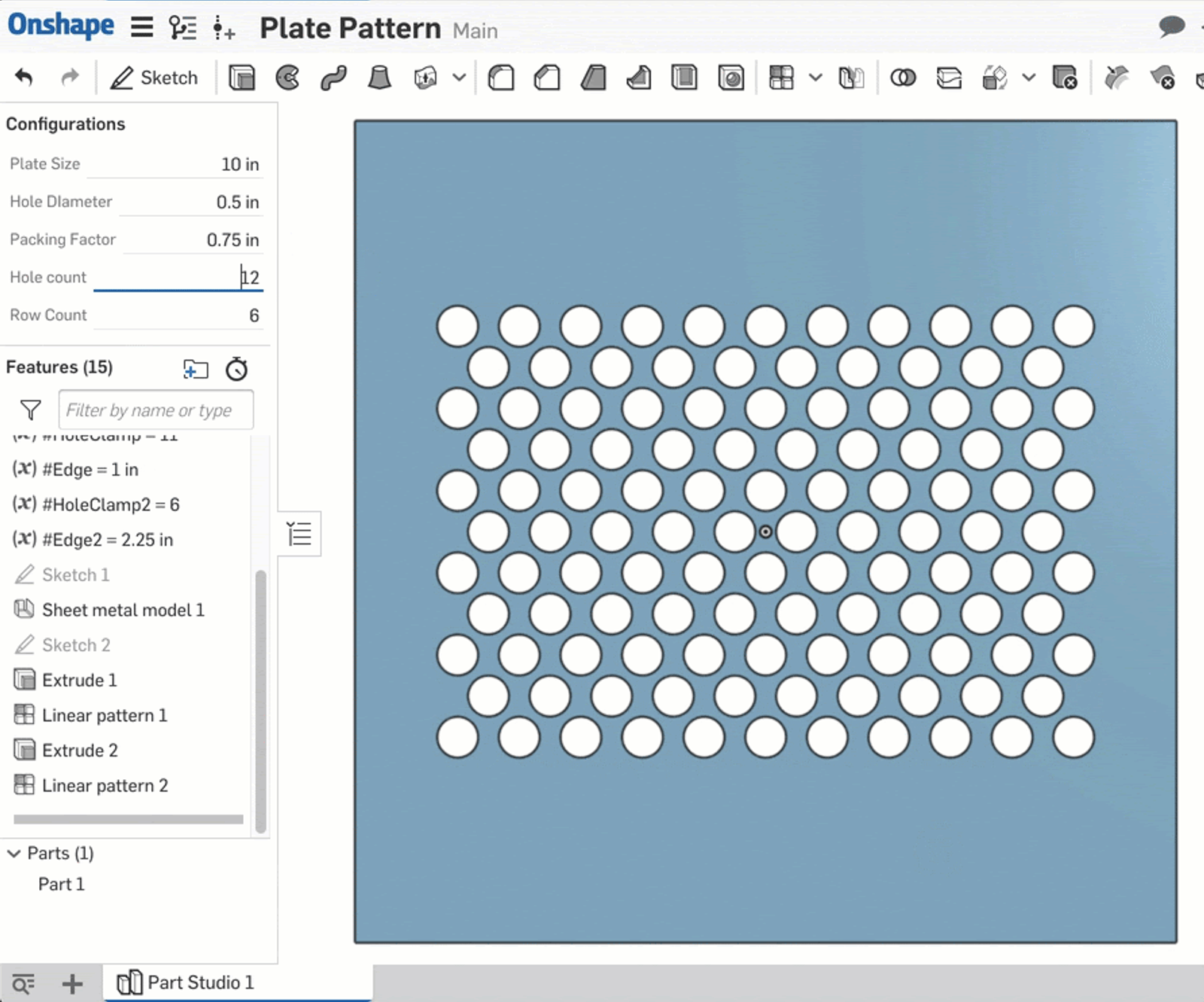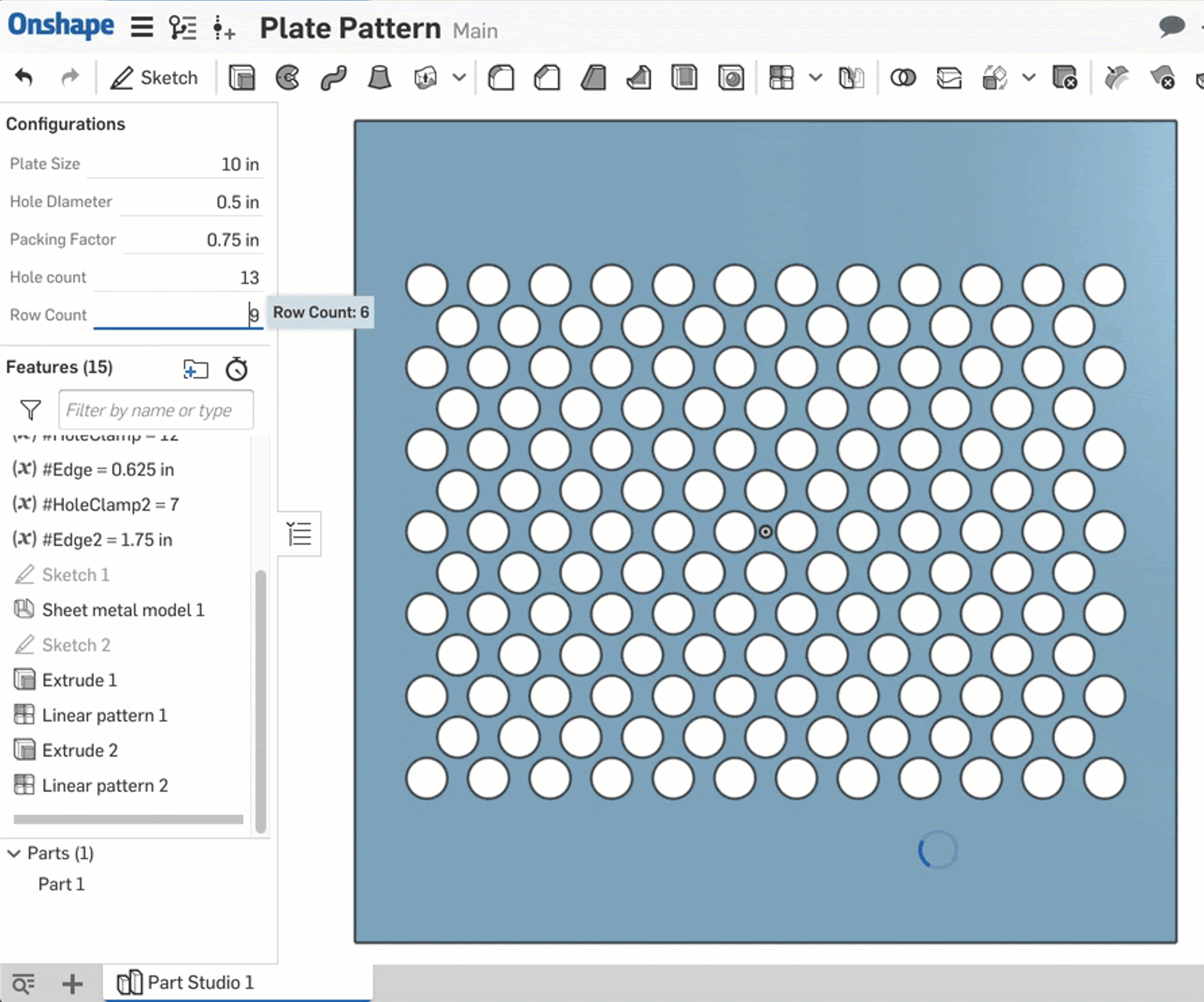
This is one example of how to combine numeric fields with other design drivers with Onshape. Of course, all of the functions and operators listed above can be used together to drive complex shapes.
For more Onshape Tech Tips, you can review the most recent technical blogs here.
Latest Content
- Blog
- Evaluating Onshape
- Collaboration
How Onshape Fixes the Broken Promise of Model-Based Definition
02.26.2026 learn more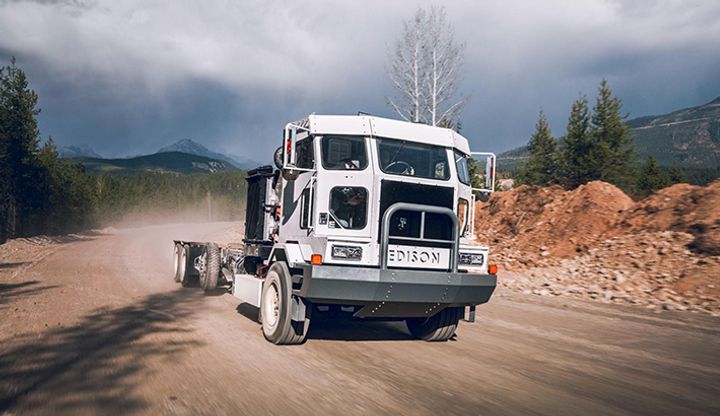
- Blog
- Customers & Case Studies
- Automotive & Transportation
Powering Heavy-Duty Innovation: How Edison Motors Builds Next-Gen Hybrid Trucks with Onshape
02.26.2026 learn more
- Blog
- Evaluating Onshape
- Education
- Education & Universities
Future-Proof Engineering Education with Model-Based Definition in Onshape
02.24.2026 learn more



