03:04
Before technology’s integration, product development typically was a long and expensive process. With digital fabrication, it has become much faster, cheaper, and agile for teams and businesses.
We see it now with the advent of Industry 4.0, which is the integration of new technology into every industry, as exemplified by Formlabs’ impact on dentistry and the use of robots in restaurants.
What is Digital Fabrication
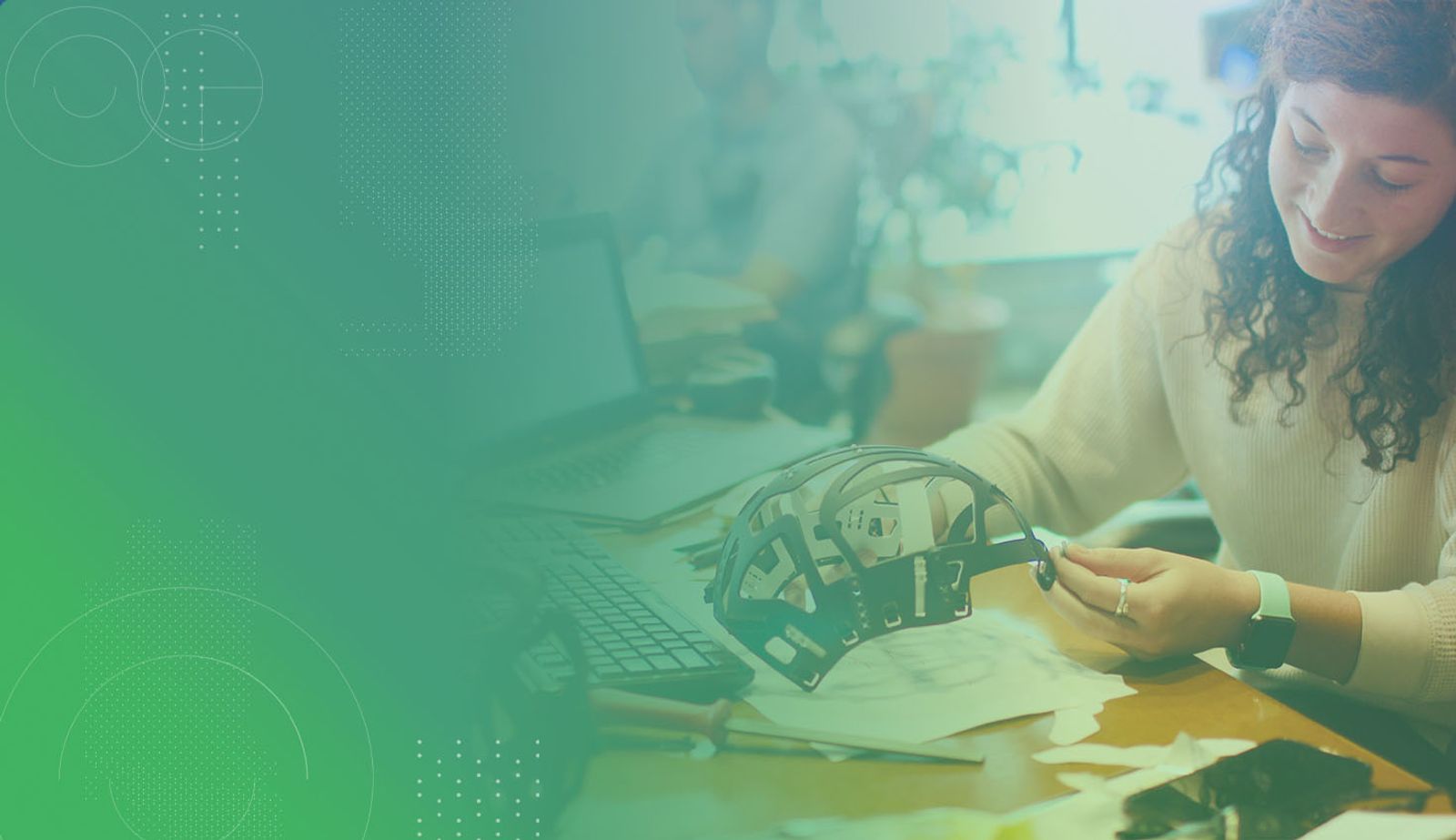
Digital fabrication is a design and manufacturing process that builds objects from computer-aided design (CAD) files. The process can be used to manufacture prototypes and small batches of parts using cheap materials, in-house, without wasting time and resources on the final product.
With rapid prototyping at hand, product developers can test the design, usability, and feasibility of a new product. It is an essential step that helps companies understand customer needs, the state of the market, and other factors that may affect the success or failure of a product.
Digital fabrication helps companies save money by reducing their need for warehouses and inventory, as well as making it easier for them to produce goods in small batches. This means companies do not need to worry about the time and cost of using outside vendors.
These reasons are driving digital fabrication’s use in industrial design, engineering, manufacturing, robotics, art, and more.
With more companies turning to digital fabrication for product development, there are more opportunities than ever to accelerate the product development process, have more flexibility in the design process, and save money.
(Courtesy: Inés Álvarez Fdez/Unsplash.com)
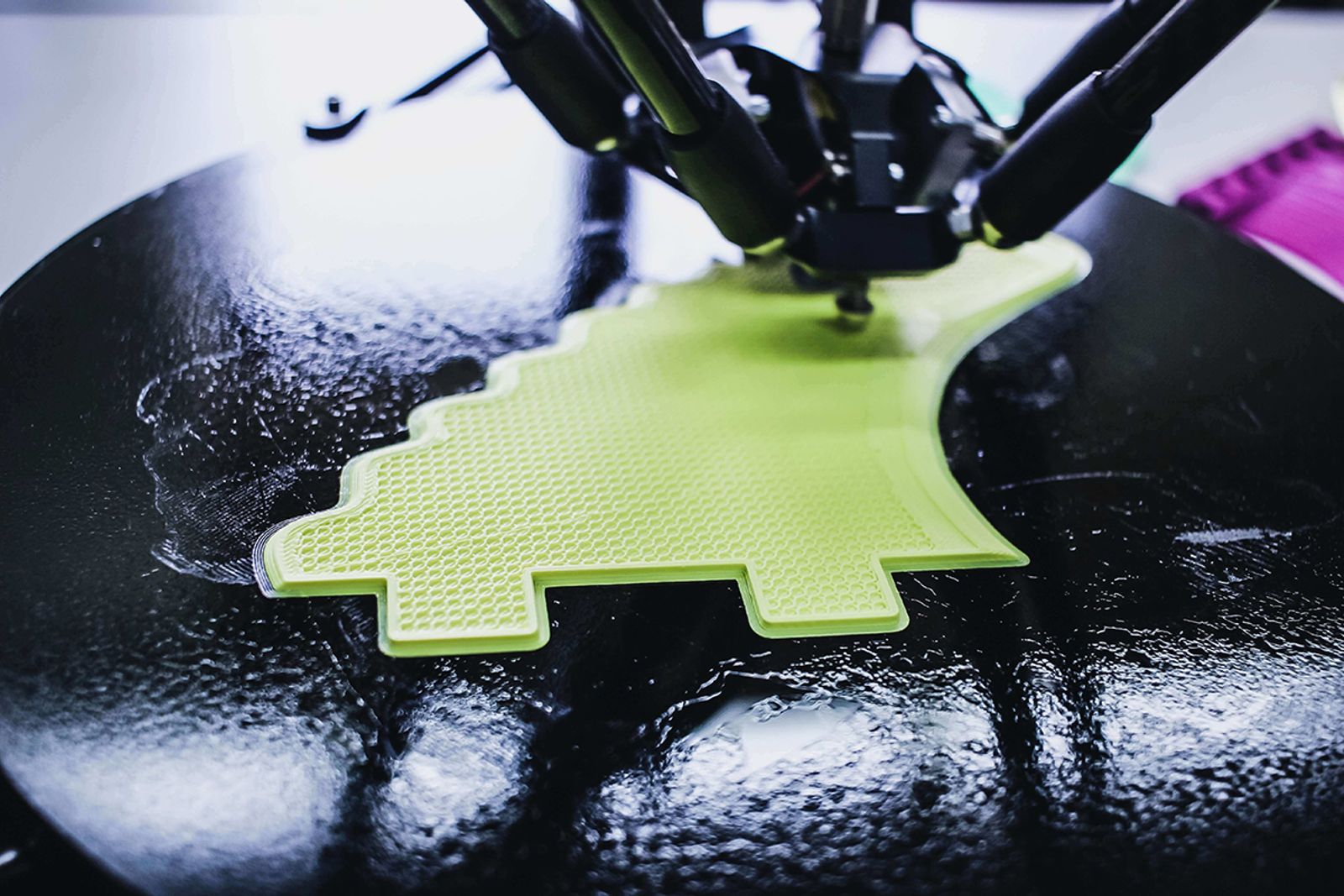
3 Popular Digital Fabrication Techniques
It is only recently that digital fabrication technologies have started to see wider adoption due to cheaper, more user-friendly machines and software, as well as an increase in demand for these technologies.
The three most popular digital fabrication techniques are 3D printing, laser cutting, and CNC (computer numerical control) milling.
Use Case for Digital Fabrication
In the eBook, Accelerating Product Development with 3D Printing and Cloud-Native CAD, three companies share how they are able to achieve quicker prototyping processes and agile workflow with the integration of digital fabrication methods.
Sam Holland of Informal, an engineering collective, has implemented digital fabrication techniques into his design workflow.
Using inexpensive plastic printing in the earlier stages speeds up the prototyping process considerably compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
“If I have an error in an injection-molded plastic part, it can take between three weeks and a month and a half to fix the issue in the molds,” Holland said. “But if I have 3D-printed parts prior to that and assemble them, I can catch the problem within a day or two. So every issue you find with the 3D prints could theoretically save you a month of time later on.”
Holland adds that making quick 3D prints of his projects also helps him rethink his CAD models in the earliest stages.
(Courtesy: @optlasers/Unsplash.com)
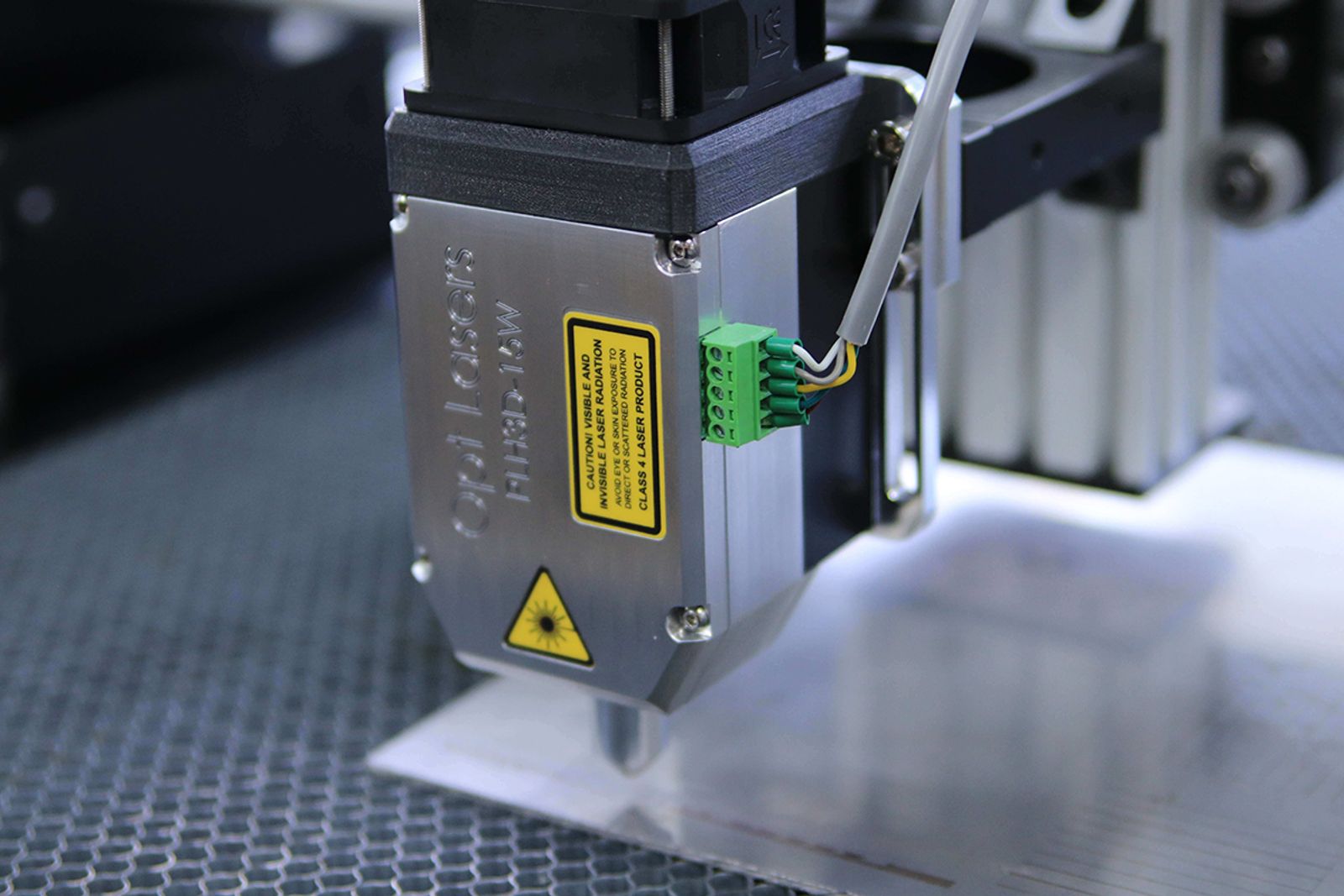
Digital Fabrication and CAD
Product development, which had once been a long and tedious process, is now becoming more streamlined than ever. With digital fabrication practices, companies can now begin the product development process in-house instead of outsourcing it to other companies.
The combination of cloud-native CAD and 3D printing is already enabling amazing innovations and speed-to-market for forward-thinking product companies.
Learn how Onshape can help your team implement agile workflows and leverage today’s technology today.
Try Onshape Today
Head to our sign-up page to choose the right CAD plan for you and your team.
(Content Marketing Specialist Rachel Valerio contributed to this blog.)
Latest Content

- Case Study
- Aviation, Aerospace & Defense
Dufour Aerospace Accelerates Critical Cargo Drone Delivery with PTC’s Onshape and Arena
02.11.2026 learn more
- Blog
- Evaluating Onshape
- Collaboration
How Onshape Fixes the Broken Promise of Model-Based Definition
02.26.2026 learn more
- Blog
- Customers & Case Studies
- Automotive & Transportation
Powering Heavy-Duty Innovation: How Edison Motors Builds Next-Gen Hybrid Trucks with Onshape
02.26.2026 learn more
- Blog
- Evaluating Onshape
- Education
- Education & Universities
Future-Proof Engineering Education with Model-Based Definition in Onshape
02.24.2026 learn more


